How Endogenous Retroviruses-K Contribute To Human Cancer ??
- Vishwanth M

- Feb 16, 2023
- 1 min read
Updated: Mar 3, 2023
Author : Vishwanth M ( Btech Biotechnology)
Over 8% of the human genome is made up of known human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs). Even though the human genome demonstrates highly controlled HERV production, several external and endogenous triggers may nonetheless cause HERV activation. The abnormal expression of different HERVs may act as a trigger for a variety of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, neurological diseases, and autoimmune diseases. HERV-K is thought to be able to cause cancer in a number of ways.
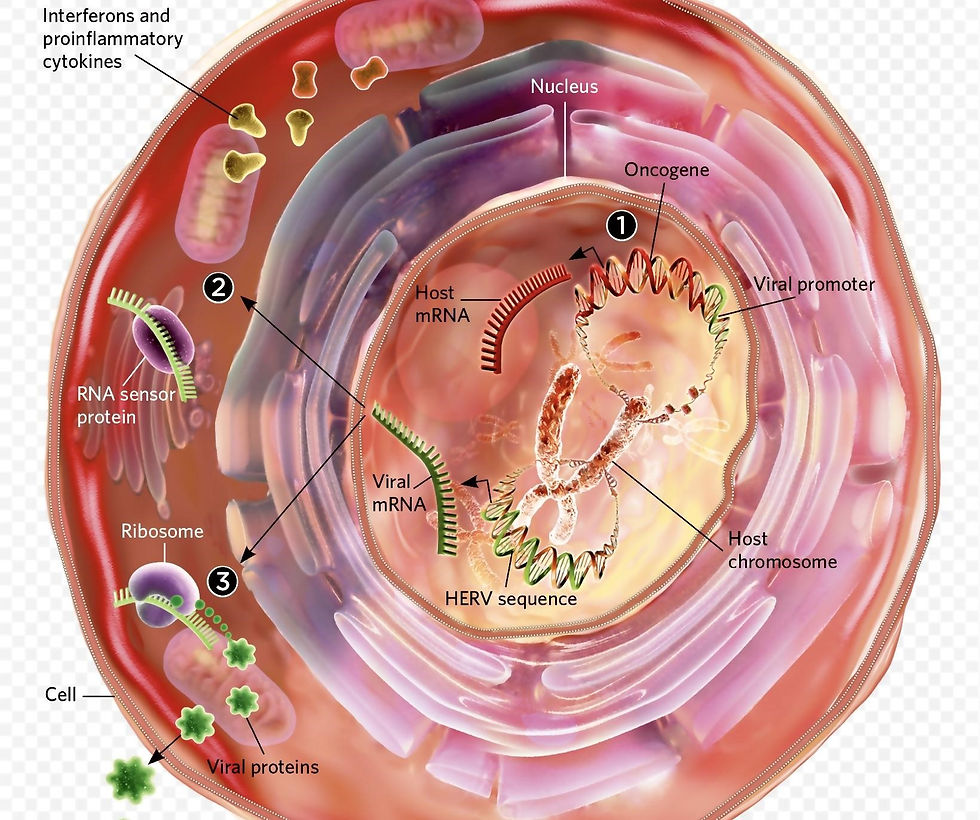
The connection between some tumour viruses and HERV-K appears to be a significant element in the development of virally associated cancers because greater levels of Rec and Np9 proteins are detected in a range of malignancies. The frequent overexpression of HERV proteins and some specific antibodies in cancer cells may be useful as prognostic and therapeutic biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Cancer immunotherapy may potentially use the appearance of immune responses against tumours and the expression of the HERV protein as targets. Research is needed because of the importance of HERVs in the emergence of cancer and the use of different HERV proteins in developing novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for cancer therapies.
References:









Comments